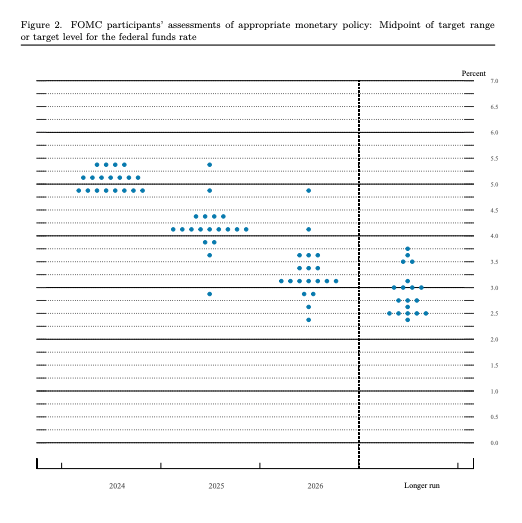
The FOMC's dot plot is a significant tool used by the Federal Reserve to communicate its members' projections for future interest rates. This chart, which is updated quarterly as part of the Summary of Economic Projections, visually represents where each Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) member believes the federal funds rate will be at the end of each year over a specified timeframe.
Importance of the Dot Plot
- Transparency and Guidance: The dot plot was introduced in 2012 to enhance transparency regarding the Fed's monetary policy decisions. It helps market participants understand the Fed's outlook on interest rates, which can influence economic behaviors and expectations.
- Market Expectations: The dot plot serves as a benchmark for market participants, offering insights into potential future monetary policy shifts. Investors, economists, and analysts closely monitor the median dot, as it reflects the collective view of the FOMC regarding the appropriate level of interest rates.
- Economic Indicators: The positioning of the dots can indicate the Fed's stance on inflation, economic growth, and employment. For instance, a clustering of dots at higher interest rates may suggest concerns about inflation, while lower projections could indicate a focus on stimulating economic growth.
Limitations and Criticisms
Despite its significance, the dot plot has faced criticism regarding its predictive accuracy:
- Variability of Projections: The projections can change significantly from one quarter to the next based on evolving economic conditions. For example, recent updates have shown a shift from expectations of multiple rate cuts to just one, reflecting the Fed's response to persistent inflation.
- Anonymous Nature: Each dot represents an individual FOMC member's view, but the anonymity of the dots makes it difficult for market participants to gauge the weight of each member's opinion. This can lead to confusion about the overall consensus.
- Potential Misleading Signals: Some economists argue that the dot plot may lead market sentiment in misleading directions, as it does not always accurately reflect future economic realities. Surveys indicate that a significant portion of market participants believe the dot plot should be revised or eliminated due to its ambiguous nature.
How Reliable Have Past Dot Plots Been in Predicting Actual Interest Rate Changes
The reliability of the FOMC's dot plot in predicting actual interest rate changes has been a topic of considerable debate. While the dot plot serves as a tool for conveying the Federal Reserve's members' expectations regarding future interest rates, its historical accuracy in forecasting actual rate movements has been mixed.
Key Points on Reliability
- Mixed Track Record: Historical assessments indicate that while some dot plot predictions have been accurate, others have significantly missed the mark. Economic conditions can change rapidly due to unforeseen events, leading to revisions in forecasts that may not align with earlier projections.
- Market Interpretation Issues: Many market participants misinterpret the dot plot, often viewing the median projection as a commitment rather than a forecast. This misunderstanding can lead to exaggerated market reactions and volatility, as investors may act on perceived promises of future rate changes.
- Influence of Economic Data: The dot plot is heavily influenced by economic indicators such as inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates. However, these indicators can be unpredictable, complicating the accuracy of the projections. As a result, the dot plot may reflect a snapshot of expectations that quickly become outdated.
- Calls for Improvement: Critics have suggested that the dot plot should be reevaluated or modified to improve clarity. Some propose linking individual projections to specific economic forecasts to better convey the rationale behind the rates, which could help mitigate confusion and enhance understanding of the inherent uncertainties in the predictions.
- Forward Guidance Role: Despite criticisms, the dot plot has been effective in providing forward guidance, helping to shape market expectations and avoid sudden shocks. It serves as a communication device that reflects the collective sentiment of the FOMC, although it may not always capture the nuances of economic dynamics.
What Are the Main Reasons for the Variability in the Dot Plot's Accuracy?
The variability in the accuracy of the FOMC's dot plot can be attributed to several key factors:
- Complexity of the Economy: The economy is influenced by a multitude of dynamic factors, including inflation rates, employment figures, and global economic conditions. This complexity makes it challenging for FOMC members to predict future interest rates accurately, as unforeseen events can significantly alter economic trajectories.
- Changing Economic Conditions: Economic conditions can shift rapidly, often in response to external shocks such as financial crises, geopolitical events, or pandemics. For instance, the dot plot from December 2019 projected no rate changes for 2020, but the COVID-19 pandemic led to drastic rate cuts, highlighting how quickly economic realities can change.
- Disagreement Among FOMC Members: The dot plot reflects individual forecasts from FOMC members, which can vary widely. This disagreement can stem from differing interpretations of economic data or varying views on the appropriate policy response. The dispersion of the dots indicates the level of consensus or discord among members, with greater variability suggesting less agreement on the economic outlook and policy direction.
- Lag in Data and Information: The dot plot is based on data available at the time of its release, which may not capture the most current economic developments. As new information emerges, the FOMC's views may shift, but the dot plot does not always reflect these changes immediately, leading to potential inaccuracies in projections.
- Market Reactions and Expectations: The dot plot can influence market expectations, but those expectations can also affect the FOMC's decisions. If markets react strongly to a dot plot, it may prompt the FOMC to adjust its policy stance, further complicating the relationship between the dot plot and actual interest rate changes.
- Historical Inaccuracies: Past dot plots have shown a tendency to overestimate or underestimate the trajectory of interest rates. For example, during periods of economic expansion, the Fed has often projected higher rates than ultimately realized, while in times of crisis, it has had to make more significant cuts than anticipated.
Conclusion
In summary, the FOMC's dot plot is a crucial tool for predicting future interest rates and understanding the Fed's monetary policy direction. It provides valuable insights into policymakers' expectations, helping to shape market behavior. However, its limitations and the inherent uncertainty of economic forecasting necessitate a cautious interpretation of the projections it presents.
- How Low Will Interest Rates Go?
- Interest Rate Predictions for the Next 3 Years: (2024-2026)
- Interest Rate Predictions for Next 2 Years: Expert Forecast
- Interest Rate Predictions for Next 10 Years: Long-Term Outlook
- When is the Next Fed Meeting on Interest Rates?
- Interest Rate Cuts: Citi vs. JP Morgan – Who is Right on Predictions?
- More Predictions Point Towards Higher for Longer Interest Rates



